This is the quiz for this beads embroidery topic and here are the link……..
https://play.kahoot.it/#/k/bd7f97d0-91d9-4c39-9eda-bd8eaae978e9
ENJOY!!!!!!

This is the quiz for this beads embroidery topic and here are the link……..
https://play.kahoot.it/#/k/bd7f97d0-91d9-4c39-9eda-bd8eaae978e9
ENJOY!!!!!!
Question :
Answer :
1. List format audio

2. Differentiate lossy and loseless.
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | LOSSY COMPRESSION | LOSSLESS COMPRESSION |
| Meaning |
|
|
| Algorithm |
|
|
| Used in |
|
|
| Application |
|
|
| Data-holding capacity of the channel |
|
|
Question :
1. Define the meaning of aperture, shutter speed, ISO and DOF
2. Differentiate the purpose of camera angles and shots.
Answer :
1. Define the meaning of aperture, shutter speed, ISO and DOF
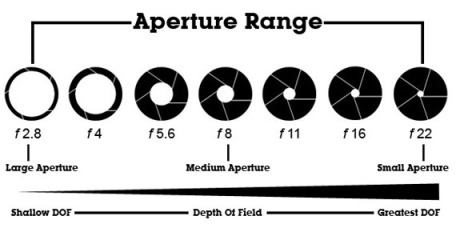
Aperture
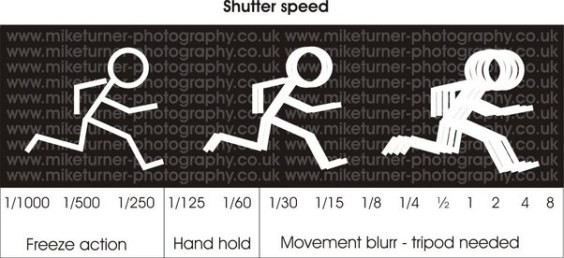
Shutter Speed
ISO
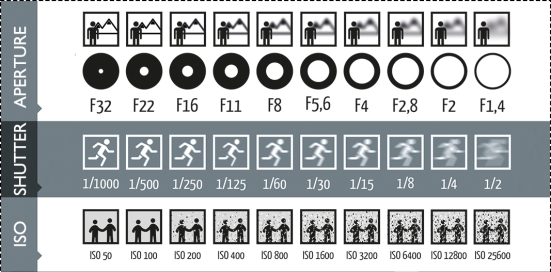
Depth of Fields

2. Differentiate the purpose of camera angles and shots.
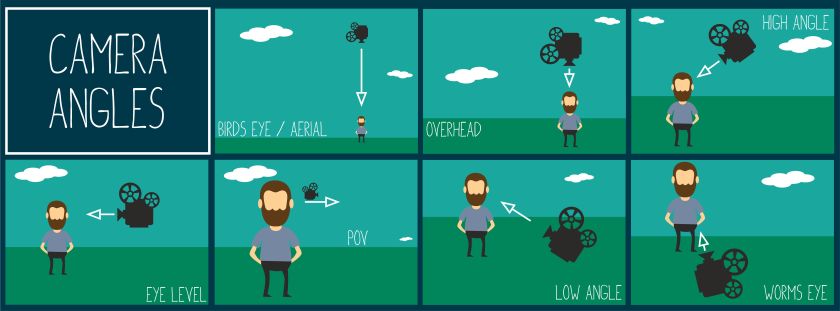
CAMERA SHOTS

1. Compare and contrast teacher vs student centered learning strategies.
2. Use table to compare and contrast the advantages and limitation of :
a. Cooperative learning
b. Gamification
c. Discovery learning
d. Inquiry-based learning
e. Project/Problem based learning
ANSWER
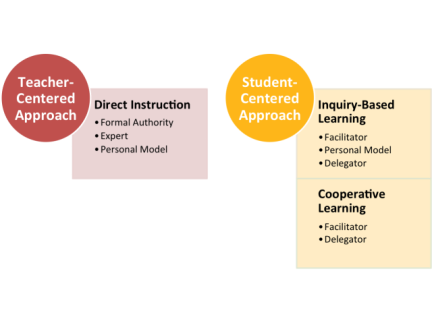
1. Compare and contrast teacher vs student centered learning strategies.
Student-centered instruction. When a classroom operates with student-centered instruction,students and instructors share the focus. Instead of listening to the teacher exclusively, students and teachers interact equally. Group work is encouraged, and students learn to collaborate and communicate with one another.
Teacher-centered education
In teacher-centered education, students put all of their focus on the teacher. You talk, and the students exclusively listen. During activities, students work alone, and collaboration is discouraged.
Pros
Student-centered instruction
When a classroom operates with student-centered instruction, students and instructors share the focus. Instead of listening to the teacher exclusively, students and teachers interact equally. Group work is encouraged, and students learn to collaborate and communicate with one another.

2.0 Use table to compare and contrast the advantages and limitation of :
a. Cooperative learning
b. Gamification
c. Discovery learning
d. Inquiry-based learning
e. Project/Problem based learning
| Aspect | Advantages | Limitation |
| · Cooperative learning | Allows students to actively participate in problem solving processes by brainstorming, discussion and presentation.
· Develop high critical thinking
|
· Requires discipline. Some learner may not participate in the group work but still get credits. |
| · Gamification | Promotes team learning and collaborative skills
· Instill confidence within students through the challenges |
· Can create anger disappointment in-group or out group.
|
| · Inquiry- based Learning | · Allows for focused learning that eliminates irrelevant aspects· Provide immediate feedback | · Can be expensive· Have limitation for number of people in the same time. |
| · Discovery Learning | · Encourages motivation, active involvement and creativity· Ensures high level of memory | · Endless wandering and seeking for answer, might be confusing· Teachers needs to be well prepared |
| · Problem Based Learning | · Develop critical thinking· Greater output
· Communication is improved |
· Unhealthy competition-while we eager to express our ideas, others opinion may be ignored. |
Define cyber learning with example of classroom application.
• Describe cyber leaning literacy and its implementation in classroom.
• Identify three web 2.0 resources.
ANSWER :

1. Define cyber learning with example of classroom application.
Definition
Classroom Application
2.Describe cyber leaning literacy and its implementation in classroom.
Definition
Implementation in classroom
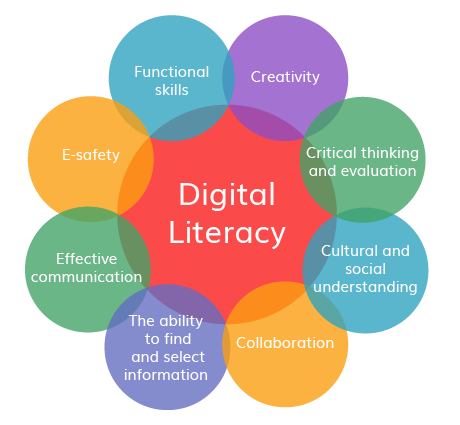
3.Identify three web 2.0 resources

Storybirds
This is a fun and easy-to-use tool for creating short, visual stories. Students can select artwork, drag and organize photos, and add their own text. These creations can then be published on the web with adjustable privacy settings. There is also the option to allow comments, which is perfect for teachers to encourage student collaboration.
Wetoku
Wetoku is a web service or Web 2.0 tool out of Korea that provides a simple platform for interviewing someone via the Internet. Collaborating globally is a must for our students and connecting can be a challenge. Wetoku makes doing an interview as easy as filling out some basic information, creating an interview session and then sending the creative interview session’s URL to the interviewee. Once the recording is done, the interviewer can embed the copy of the URL into a blog or website. You will need a web-cam to use this tool.
Skype
This web tool is an easy solution for teachers to open up their classroom and their students to a world way beyond their campus. With Skype, students can learn from other students, connect with other cultures, and expand their knowledge in amazing ways by communicating through their computer with a webcam.
The ASSURE model is the process of designing a modified teaching system for use by teachers in the regular classroom.
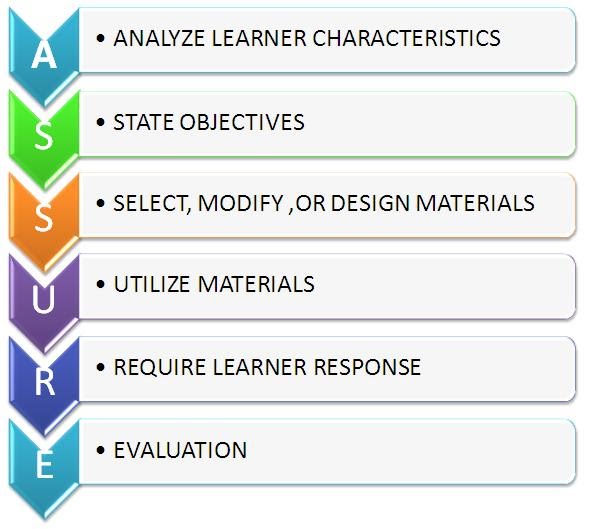
2. Why are learning objectives is important
Learning Objectives
Every program of instruction, course, or training activity begins with a goal. This goal can be broken down into specific goals, or learning objectives, which are concise statements about what students will be able to do when they complete instruction.
Why are learning objectives important?
The philosopher Seneca once said, “If one does not know to which port one is sailing, no wind is favorable.” When you know where you are headed, you can more easily get there. Well-defined and articulated learning objectives are important because they:
3. What are the four component crafting a good learning objectives?
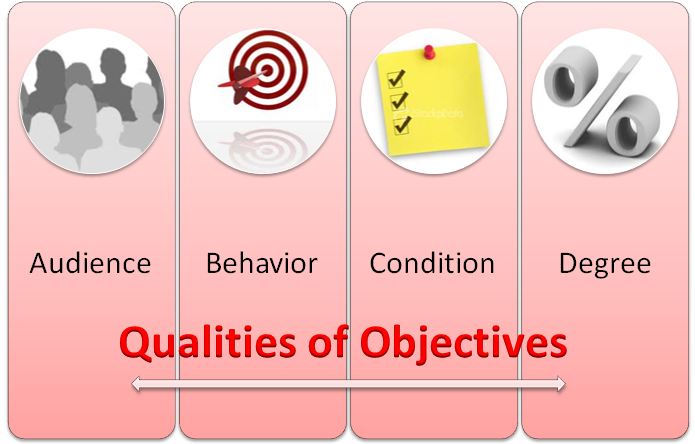
A – Audience
Every learning objective should state something that the learner should do. Sometimes, your objective may refer to the “actor” in general terms such as “the learner” or “you.” Other times, you may identify the actor by his or her job role, such as “the customer service representative” or “the press operator.” Regardless, remember that each learning objective states something that the actor must be able to do after the training. This is the “WHO?” of your objective.
B – Behavior
Every learning objective should state something that the learner must do—a behavior of some sort. This may be something as simple as stating a definition or it may be something more “physical,” such as performing an action. But it must be some form of observable behavior, not something unobservable like “know,” “understand,” or “appreciate.” This is the “WHAT?” of your objective.
3. C – Condition
Many times, your learner will have to perform the learning objective’s behavior within a set of given conditions. For example, you might say “given a list of words, circle the ones that are part of a given machine,” or “given a wrench, tighten this bolt,” or “given a schematic diagram, correctly identify the machines in a work area.” This is the “HOW?” of your objective.
4. D – Degree
This part of the learning objective explains the criteria for performing the task well enough. Examples here include “in less than ten minutes,” or “with 90% accuracy,” or “90 times an hour.” This is the “HOW WELL?” of your objective.
This is the introduction about beads embroidery project where you have to know about the task given. I have prepared the video about the introduction of task/project given to you. This video contains of topic summary and learning objective.
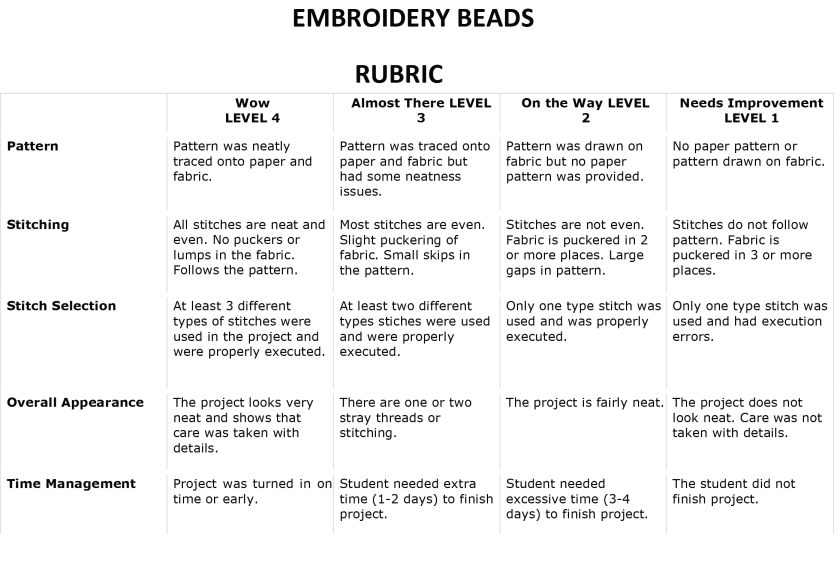
A scoring rubric is an attempt to communicate expectations of quality around a task. This rubric will be a guide by students when planning their work. Here is the rubric for your guideline in producing beads embroidery technique.